hacer un programa que le hasta 30 edades y reporte la mayor edad y la menor edad y el preomedio de edades.
codigo:
import java.io.*;
public class Vecto {
/**
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
int edades[] =new int [30];
int n=0, suma=0, cmay=0, cmen=0;
do{
System.out.println("");
n=leerEntero("ingrese el numero de edades: ");
}while(n<0 || n>30);
for( int i=0; i<n; i++){
do{
edades[i]=leerEntero("ingrese edad");
}while(edades[i]<0 || edades[i]>120);
}
int edadmenor=edades[0];
for( int i=0; i<n;i++){
suma +=edades[i];
if(edades[i]<18)cmen++;
if(edadmenor>edades[i]) edadmenor=edades[i];
}
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
System.out.println("edad["+i+"]:" + edades[i]);
}
System.out.println("el promedio de la edad es : "+suma/n);
System.out.println("la cantidad de personas mernores es: "+cmen);
System.out.println("la cantidad de personas mayores es: "+(n -cmen));
System.out.println("la edad menor es:"+edadmenor);
}
static int leerEntero(String mensaje)throws IOException{
BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader (new InputStreamReader (System.in));
int x;
System.out.println(mensaje);
x=Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
return x;
}
}
ejercicio 5( (guia)
Dado un valor N, muestre los numeros pares y numeros impares que existen entre 1 y N codigo:
import java.io.*;
public class Vecto {
/**
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
int edades[] =new int [30];
int n=0, suma=0, cmay=0, cmen=0;
do{
System.out.println("");
n=leerEntero("ingrese el numero de edades: ");
}while(n<0 || n>30);
for( int i=0; i<n; i++){
do{
edades[i]=leerEntero("ingrese edad");
}while(edades[i]<0 || edades[i]>120);
}
int edadmenor=edades[0];
for( int i=0; i<n;i++){
suma +=edades[i];
if(edades[i]<18)cmen++;
if(edadmenor>edades[i]) edadmenor=edades[i];
}
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
System.out.println("edad["+i+"]:" + edades[i]);
}
System.out.println("el promedio de la edad es : "+suma/n);
System.out.println("la cantidad de personas mernores es: "+cmen);
System.out.println("la cantidad de personas mayores es: "+(n -cmen));
System.out.println("la edad menor es:"+edadmenor);
}
static int leerEntero(String mensaje)throws IOException{
BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader (new InputStreamReader (System.in));
int x;
System.out.println(mensaje);
x=Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
return x;
}
}
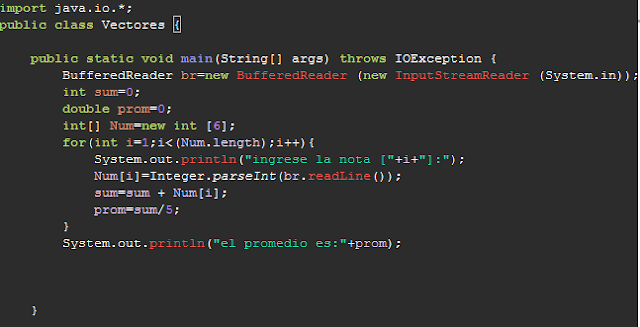
Escribir un programa que lea las notas de n alumnos y reporte lo siguiente:
1.La nota promedio.
2.Todos los datos ingresados
codigo:
import java.io.*;
public class Vectores {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader (new InputStreamReader (System.in));
int sum=0;
double prom=0;
int[] Num=new int [6];
for(int i=1;i<(Num.length);i++){
System.out.println("ingrese la nota ["+i+"]:");
Num[i]=Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
sum=sum + Num[i];
prom=sum/5;
}
System.out.println("el promedio es:"+prom);
}
}
public class Vectores {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader (new InputStreamReader (System.in));
int sum=0;
double prom=0;
int[] Num=new int [6];
for(int i=1;i<(Num.length);i++){
System.out.println("ingrese la nota ["+i+"]:");
Num[i]=Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
sum=sum + Num[i];
prom=sum/5;
}
System.out.println("el promedio es:"+prom);
}
}
ejercicio 5( (guia)
import java.io.*;
public class ejercicico05 {
public static void main(String[] args)throws IOException{
BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
System.out.println("ingrese el numero");
int n,i;
n=Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
System.out.println("*los numeros pares son ");
for(i=1; i<=n; i++)
if(i%2==0)
System.out.println(i);
System.out.println("*los numeros impares son ");
for(i=1; i<=n; i++)
if(i%2!=0)
System.out.println(i);
}
}
import java.io.*;
public class SueldoA {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException
{BufferedReader br= new BufferedReader (new InputStreamReader(System.in));
double desA, desB, desC,Xsol, SueldoNeto;
System.out.println("ingrese el sueldo";
Xsol=Double.parseDouble(br.readLine());
desA=(0.05)*100;
desB=(0.12)*100;
desC=(0.15)*100;
SueldoNeto=Xsol-(desA+desB+desC);
System.out.println("el descuento por AFP ="+desA);
System.out.println("el descuento por ESSALUD ="+desB);
System.out.println("el descuento por AFP2"+desC);
System.out.println("el sueldo neto es = "+SueldoNeto);
}
}
Ejercicios sobre operaciones Básicas
import java.io.*;
public class Ejercicio03 {
public static void main(String[] args)throws IOException
{BufferedReader br= new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
int n1, n2,suma,resta,produc,div;
System.out.println("escriba el numero 1"
n1=Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
System.out.println("escriba el numero 2"
n2=Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
suma=n1+n2;
resta=n1-n2;
produc=n1*n2;
div=n1/n2;
System.out.println("la suma = "+suma);
System.out.println("la resta = "+resta);
System.out.println("el producto = "+produc);
System.out.println("la division = "+div);
}
}
Condicionales
import java.io.*;
public class jerci01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws
IOException {BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader (new InputStreamReader(System.in));
double nota;
nota=Double.parseDouble(br.readLine());
if (nota>=10.5)
System.out.println("aprobado");
else
System.out.println("desaprobado");
}
}
otra forma
import java.io.*;
public class jerci01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws
IOException {BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader (new InputStreamReader(System.in));
System.out.println("ingrese la nota");
double nota;
nota=Double.parseDouble(br.readLine());
if (nota>=0 && nota<10.5)
System.out.println("desaprobado");
else
System.out.println("aprobado");
}
}
import java.io.*;
public class ejerc4 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException
{BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader (new InputStreamReader(System.in));
System.out.println("ingrese los numeros");
int a, b ;
System.out.println("ingrese el numero 1 ");
a=Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
System.out.println("ingrese el numero 2");
b=Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
if (a==b)
System.out.println(" estos numeros son iguales");
else if (a>b)
System.out.println(a+" es mayor que " +b);
else
System.out.println(b+ " es mayor que " +a);
}
}
Ejemplo: Ingresar 3 números enteros
positivos e indicar cual es el mayor
import java.io.*;
public class prueba4 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException
{BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader (new InputStreamReader(System.in));
int x, y, z;
System.out.println("ingrese el numero 1");
x=Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
System.out.println("ingrese el numero 2");
y=Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
System.out.println("ingrese el numero 3");
z=Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
if (x>y)
if (x>z)
System.out.println("el mayor es "+x );
else
System.out.println("el mayor es "+z);
else
if (y>z)
System.out.println("el mayor es "+y);
else
System.out.println("el maoyor es "+z);
}
}
Ejemplo: Dado un numero, determinar el mes .
import java.io.*;
public class SwitchCase {
public static void main(String[] args)throws IOException
{BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader (new InputStreamReader (System.in));
byte mes;
System.out.println("ingrese el mes del 1 al 12");
mes=Byte.parseByte(br.readLine());
switch (mes)
{ case 1:System.out.println("enero");break;
case 2:System.out.println("febreo");break;
case 3:System.out.println("marzo");break;
case 4:System.out.println("abril");break;
case 5:System.out.println("mayo");break;
case 6:System.out.println("junio");break;
case 7:System.out.println("julio");break;
case 8:System.out.println("agosto");break;
case 9:System.out.println("septiembre");break;
case 10:System.out.println("octubre");break;
case 11:System.out.println("noviembre");break;
case 12:System.out.println("diciembre");break;
default:System.out.println("incorrecto");break;
}
}
}
EJERCICIO Nº2 Escribir un programa que lea N numeros y reporte suma. Plantear la solucion utilzando: While, do While, y for.
codigo:
import java.io.*;
public class Ejercicio03Guia {
/**
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args)throws
IOException{BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader (new InputStreamReader(System.in));
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("ingrese el numero y resione -1 para terminar");
double N;
double suma=0;
do{
N=Double.parseDouble(br.readLine());
if(N<0) break;
suma = suma + N;
}while (true);
System.out.println("sum=" +suma);
}
}
Ejercicio nº4 leer N numeros e indicar cuantos son positivos y negativos
import java.io.*;
public class javas {
public static void main(String[] args)throws IOException
{BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader (new InputStreamReader(System.in));
int n,num,c=0,cp=0,cn=0;
do{
System.out.println("ingrese la cantidad de numeros");
n=Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
}while(n<=0);
while(c<n){
System.out.println("ingrese los numeros");
num=Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
if(num!=0)
{ c=c+1;
if (num>0)
cp=cp+1;
else
cn=cn+1;}
else
System.out.println("error");
}
System.out.println("cantidad de numeros positivos");
System.out.println(cp);
System.out.println("cantidad de numeros negativos");
System.out.println(cn);
}
}
DIFERENTES TIPOS DE METODOS
ejercicio: ejercicio que lea 2 numeros y reporte el producto.
import java.io.*;
public class Ejercicio01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
int n1, n2, p;
n1 = LeeNum();
n2 = LeeNum();
p = Producto(n1, n2);
Reporte(p);
}
static int LeeNum() throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
int n;
do {
System.out.print("Ingrese numero: ");
n = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
} while (n <= 0);
return n;
}
static int Producto(int n1, int n2) {
int i, p = 0;
for (i = 1; i <= n1; i++) {
p = p + n2;
}
return p;
}
static void Reporte(int p) {
System.out.println("\nReporte");
System.out.println("-------");
System.out.println("Producto: " + p);
}
}
EJERCICIO : un ejercicio que reporte la suma, division, multiplicacion, producto en java eclipse.
import java.io.*;
public class Ejercico02 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
int n1, n2, s, r, p, d;
n1 = LeeNum();
n2 = LeeNum();
s = Suma(n1, n2);
r = Resta(n1, n2);
p = Producto(n1, n2);
d = Division(n1, n2);
Reporte(s, r, p, d);
}
static int LeeNum() throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
int n;
do {
System.out.print("Ingrese numero: ");
n = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
} while (n <= 0);
return n;
}
static int Suma(int n1, int n2) {
int i, s = 0;
for (i = 1; i <= n1; i++) {
s = n1 + n2;
}
return s;
}
static int Resta(int n1, int n2) {
int i, r = 0;
for (i = 1; i <= n1; i++) {
r = n1 - n2;
}
return r;
}
static int Producto(int n1, int n2) {
int i, p = 0;
for (i = 1; i <= n1; i++) {
p = p + n2;
}
return p;
}
static int Division(int n1, int n2) {
int i, d = 0;
for (i = 1; i <= n1; i++) {
d = n1 / n2;
}
return d;
}
static void Reporte(int s, int r, int p, int d) {
System.out.println("\nReporte");
System.out.println("-------");
System.out.println("Suma: " + s);
System.out.println("Resta: " + r);
System.out.println("Producto: " + p);
System.out.println("Division: " + d);
}
}
ejercicio que sume edades:
import java.io.*;
public class SumaEd {
/**
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args)throws IOException
{
int a,b,c,suma=0;
a=leerEnteros("edade 1");
b=leerEnteros("edade 2");
c=leerEnteros("edade 3");
suma=sumaEnteros(a,b,c);
System.out.println("la suma de edades es: "+suma);
}
static int leerEnteros(String impEdades) throws IOException
{
BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
int x;
System.out.println(impEdades);
x=Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
return x;
}
static int sumaEnteros(int q,int w,int k) {
int sum=0;
sum=q+w+k;
return sum;
}
}